Why So Many People Switched from Traditional Ways to Point Cloud Processing
Introduction
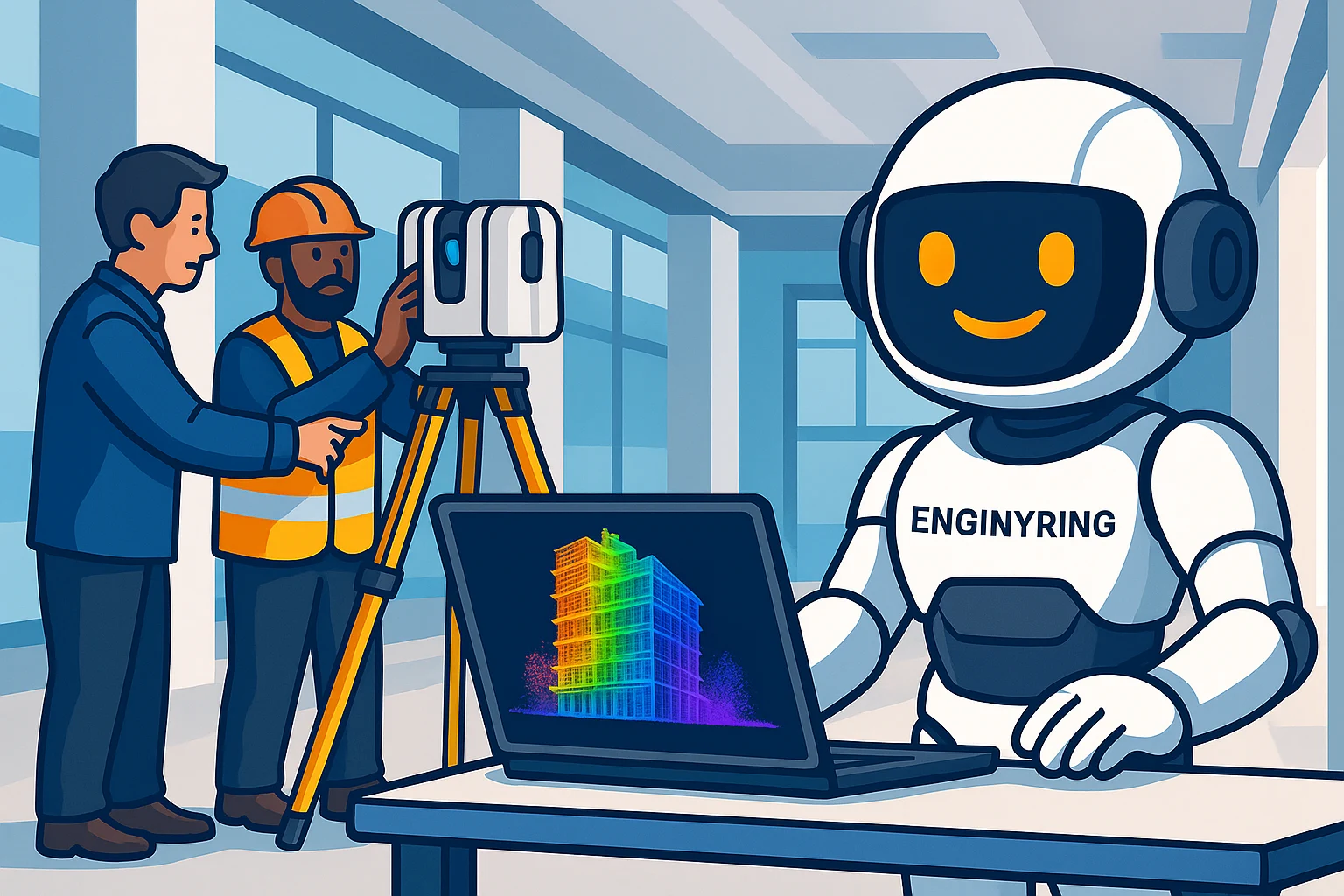
In the last decade, the architectural, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry has seen a remarkable transformation in the way spatial data is captured, managed, and utilized. A growing number of professionals and organizations are shifting from conventional measurement and documentation methods to advanced digital techniques. Among these, point cloud processing has rapidly emerged as a cornerstone technology. But what exactly is point cloud processing, and why are so many people and companies making this switch? At ENGINYRING, we aim to demystify this topic for beginners and provide a clear, thorough explanation of why point cloud processing is reshaping the industry.
Understanding Traditional Measurement and Documentation Methods
Traditionally, the capture of building dimensions and spatial data has relied on manual measurement tools such as tape measures, total stations, and levels. Field survey teams would often spend hours or days on-site, meticulously documenting measurements, taking photographs, and making hand-drawn sketches. This data would then be transferred to paper plans or digitized in 2D CAD software.
- Manual measurements: Labor-intensive and susceptible to human error
- Hand sketches: Prone to inaccuracies and misinterpretations
- Photographs: Offer limited spatial information without precise coordinates
- 2D CAD drafting: Time-consuming and often based on incomplete field data
While these methods have served the industry for decades, they present significant challenges in today’s fast-paced, technology-driven environment. These challenges include lengthy project timelines, increased labor costs, risk of data loss, and frequent need for return site visits due to missing or inaccurate information.
What Is Point Cloud Processing?
Point cloud processing refers to the collection, management, and analysis of millions or even billions of spatial data points generated by laser scanners or photogrammetry systems. Each point in a point cloud represents a precise position in three-dimensional space, creating a highly detailed digital replica of an object, building, or environment.
- Data capture: Performed with 3D laser scanners, drones, or cameras, resulting in a ‘cloud’ of points
- Processing: Involves filtering, aligning, and converting raw point data into usable 3D models
- Output: Point clouds are used as the basis for accurate 2D drawings, 3D models, and Building Information Models (BIM)
The ability to quickly and precisely record complex physical spaces has become a game-changer for architecture, engineering, construction, and facility management. At ENGINYRING, we specialize in point cloud processing to support our clients with state-of-the-art digital solutions.
The Key Drivers Behind the Shift to Point Cloud Processing
Several factors have contributed to the widespread adoption of point cloud processing in the AEC sector and beyond. Let’s explore the most important drivers of this transition:
1. Enhanced Accuracy and Precision
Laser scanners and photogrammetry systems are capable of capturing millions of points within seconds, providing a level of detail and accuracy that is virtually impossible to achieve with manual measurement techniques. This results in:
- Reduced errors: Highly accurate spatial data minimizes the risk of costly design or construction mistakes
- Reliable documentation: As-built conditions are recorded in detail, supporting precise planning and renovation
2. Increased Speed and Efficiency
Traditional measurement methods require significant time investment, especially for large or complex structures. Point cloud scanning, on the other hand, can capture entire buildings or sites in a fraction of the time. Benefits include:
- Shorter project timelines: Data collection is much faster, allowing projects to move forward without delay
- Reduced site visits: The need for repeated measurements is eliminated, saving travel and labor costs
3. Comprehensive Data Capture
Conventional methods are often limited to selected areas or features, leaving gaps in the dataset. Point clouds provide a complete, 360-degree representation of an environment, including details that may have been overlooked or inaccessible during manual surveys.
- Full coverage: Every visible surface is documented, reducing the risk of missing information
- Versatility: Data can be used for multiple purposes, such as design, construction, maintenance, and facility management
4. Improved Collaboration and Communication
Point cloud data can be easily shared and visualized in 3D, making it simpler for project teams, stakeholders, and clients to understand existing conditions and make informed decisions.
- Remote access: Teams can review and analyze data from anywhere
- Enhanced coordination: 3D visualizations promote better alignment between architects, engineers, and contractors
5. Cost Savings Over the Project Lifecycle
While the initial investment in scanning equipment and software can be significant, point cloud processing offers cost savings by reducing fieldwork time, preventing errors, and eliminating rework. These efficiencies contribute to a better return on investment (ROI) across the entire project lifecycle.
6. Facilitating Advanced Workflows: From 2D Drawings to BIM
Point clouds serve as a bridge between the physical world and advanced digital workflows. They can be converted into highly accurate 2D drawings, 3D models, and Building Information Models (BIM). This seamless transition supports design, analysis, and construction in ways that traditional documentation cannot match. For more information on how point clouds integrate with BIM, see our scan-to-BIM service.
Case Study: Comparing Traditional and Point Cloud-Based Approaches
To better understand the benefits of point cloud processing, let’s consider a practical scenario: the renovation of a historic building.
Traditional Approach
- Surveyors spend multiple days measuring each room and feature by hand
- Measurements are recorded manually, leading to potential transcription errors
- Missing or inconsistent data results in repeated site visits
- 2D drawings are produced based on best-guess interpretations of the field data
- Design and construction teams work with incomplete or outdated information
Point Cloud-Based Approach
- A 3D laser scanner captures the entire building in a single visit
- Point cloud data provides a comprehensive, highly accurate digital record
- 2D drawings and 3D BIM models are generated directly from the point cloud
- Designers, engineers, and contractors can access and review the data remotely
- Project risks and costs are significantly reduced
Applications of Point Cloud Processing
Point cloud processing has a wide range of applications beyond just building measurement and renovation. Some key use cases include:
- Heritage preservation: Documenting historic structures in fine detail for restoration and conservation
- Construction verification: Comparing as-built conditions to design models for quality assurance
- Facility management: Creating accurate digital twins for ongoing maintenance and space planning
- Infrastructure projects: Surveying bridges, tunnels, roads, and utility networks
- Industrial facilities: Capturing complex mechanical, electrical, and plumbing (MEP) systems
How Point Cloud Processing Works: A Step-by-Step Guide
Understanding the basic workflow can help beginners see why point cloud processing is so effective. Here’s a simplified overview:
- Data Acquisition:
- 3D laser scanners, drones, or cameras are used to capture millions of data points from the environment
- Each scan produces a “point cloud” that accurately represents the surfaces and features in 3D
- Registration:
- Multiple scans are aligned and merged into a single, unified point cloud
- Specialized software corrects for any positional errors and ensures seamless integration
- Cleaning and Filtering:
- Noise and irrelevant data (such as moving objects or background points) are removed
- The clean point cloud is ready for analysis and modeling
- Modeling:
- Point cloud data is used as a reference to create precise 2D drawings, 3D models, or BIM files
- Manual tracing or automated extraction tools help convert raw data into usable formats
- Output and Analysis:
- The resulting models and drawings can be used for design, construction, facility management, or analysis
- Point clouds themselves can also be visualized for inspection and measurement purposes
ENGINYRING offers comprehensive point cloud processing services, guiding clients through every stage of this workflow.
Why Beginners Should Consider Point Cloud Processing
If you are new to architectural documentation or building measurement, adopting point cloud processing can provide a competitive edge. Key reasons include:
- Simplicity: Modern scanning equipment and software are increasingly user-friendly
- Time savings: Quickly capture and model spaces with minimal training
- Scalability: Suitable for small projects as well as large, complex environments
- Future-proofing: As digital workflows become standard, point cloud skills are highly valuable
For those transitioning from hand sketches, our sketch to digital services can help bridge the gap between traditional and modern documentation methods.
Common Misconceptions about Point Cloud Processing
Despite its advantages, some professionals are hesitant to adopt point cloud processing due to misconceptions. Let’s address a few:
- “It’s only for large projects.”
Reality: Point cloud processing is valuable for projects of any size, from single rooms to entire campuses. - “It’s too expensive.”
Reality: While initial costs may be higher, the long-term savings in labor, accuracy, and risk reduction often outweigh the investment. - “It’s too complex for beginners.”
Reality: User-friendly software and professional service providers like ENGINYRING make it accessible even for those new to the field.
The Future of Spatial Data: Beyond Point Clouds
Point cloud processing is already revolutionizing how we capture and manage spatial information, but the technology continues to evolve. Integration with artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning, and automation is making it easier to extract valuable insights from point cloud data. As these advancements continue, we can expect even greater accuracy, speed, and versatility in building documentation and facility management.
At ENGINYRING, we stay at the forefront of these developments to provide our clients with best-in-class solutions that address both current needs and future opportunities.
How ENGINYRING Supports Your Transition to Point Cloud Processing
Switching to point cloud processing may seem like a daunting task, but ENGINYRING is here to guide you every step of the way. Our team offers:
- Expert advice: Consultation on the best methods and tools for your project
- Comprehensive services: From scanning to BIM modeling, tailored to your requirements
- Training and support: Assistance for teams new to point cloud workflows
- Seamless integration: We help you transition from traditional drawings or sketches to advanced digital models
Ready to embrace the future of digital documentation? Contact ENGINYRING today to discuss how our point cloud processing solutions can transform your next project.
Conclusion
The shift from traditional measurement and documentation methods to point cloud processing is a defining trend in the modern AEC industry. With benefits including unparalleled accuracy, speed, comprehensive data capture, and streamlined workflows, it’s no wonder that so many professionals and organizations are making the switch.
For those new to the field, adopting point cloud processing is more accessible than ever before. Whether you’re looking to improve efficiency, reduce costs, or future-proof your practice, point cloud technology offers a clear pathway to success. ENGINYRING is committed to helping you navigate this transition and unlock the full potential of digital spatial data.
Explore our services for point cloud processing, 2D drafting and drawing, and sketch-to-digital conversion, and discover how we can add value to your next project.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is a point cloud?
A point cloud is a collection of millions of spatial data points captured by laser scanners or photogrammetry. Each point has an X, Y, Z coordinate, representing its position in 3D space. - How accurate is point cloud processing?
Modern laser scanners can achieve millimeter-level accuracy, providing much more reliable data than manual measurements. - Can I use point cloud data for BIM?
Yes, point clouds can be used as the foundation for creating accurate Building Information Models, supporting design, renovation, and facility management workflows. - Is point cloud processing suitable for small projects?
Absolutely. Point cloud technology is scalable and offers benefits for projects of any size. - How do I get started?
Contact ENGINYRING for a free consultation and expert guidance on transitioning to point cloud processing.
🇷🇴 Cauți versiunea în română? Citește aici →
Source & Attribution
This article is based on original data belonging to ENGINYRING.COM blog. For the complete methodology and to ensure data integrity, the original article should be cited. The canonical source is available at: Why So Many People Switched from Traditional Ways to Point Cloud Processing.