Understanding Proxmox VE: The Ultimate Guide for Aspiring Hosting Professionals
In the rapidly evolving world of information technology and web hosting, virtualization stands as a cornerstone technology. It is the fundamental principle that allows for the efficient use of physical hardware, enabling the creation of dynamic, scalable, and isolated environments. For businesses and individuals stepping into the hosting industry, choosing the right virtualization platform is a critical decision. Among the myriad of options available, Proxmox Virtual Environment (VE) has emerged as a uniquely powerful, flexible, and cost-effective open-source solution. At ENGINYRING, we frequently leverage this technology to build robust infrastructures for our clients, and this guide aims to demystify Proxmox VE for beginners.
This comprehensive article will explore the core concepts of Proxmox VE, from its fundamental components to its advanced features. We will delve into what sets it apart, explain the key technologies it employs, and illustrate why it has become a preferred choice for everyone from tech enthusiasts running home labs to large-scale data centers. Whether you aim to launch a hosting business, streamline your company's IT infrastructure, or simply expand your technical knowledge, understanding Proxmox is an invaluable asset.
What is Proxmox VE?
Proxmox Virtual Environment, or Proxmox VE, is a complete, open-source server management platform for enterprise virtualization. At its heart, it is a specialized Linux distribution based on Debian, equipped with a custom kernel. Its primary function is to enable the deployment and management of virtual machines (VMs) and containers on a single physical server, or a cluster of servers. What makes Proxmox particularly appealing is that it integrates these capabilities, along with storage and network management, into a single, intuitive web-based interface.
Think of it as a centralized command center for your entire virtual infrastructure. Instead of juggling multiple tools and complex command-line interfaces to manage different aspects of your servers, Proxmox provides a unified solution. This not only simplifies administration but also reduces the potential for error and lowers the barrier to entry for managing sophisticated server environments. It effectively turns your physical hardware into a versatile pool of resources that can be allocated on-demand to create fully isolated digital systems.
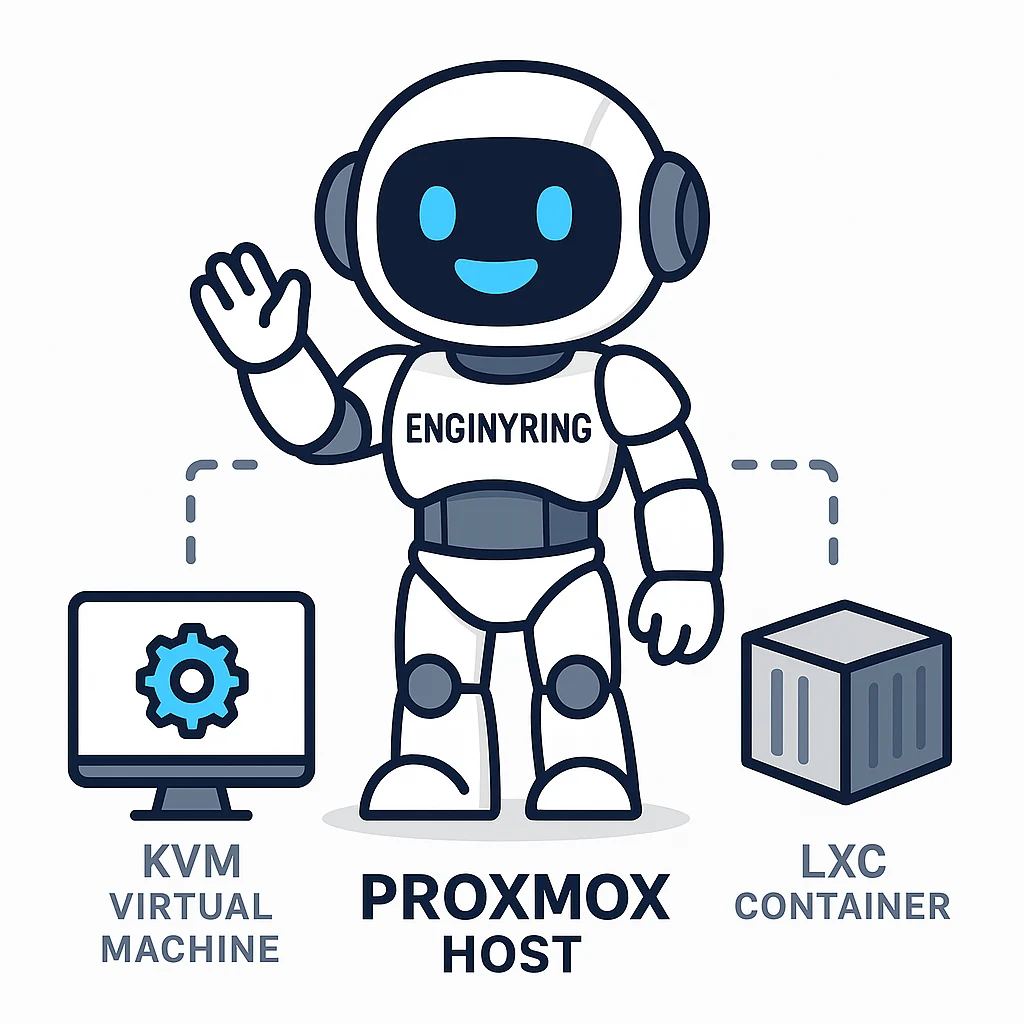
The Core of Proxmox: KVM and LXC Explained
Proxmox VE's power comes from its integration of two distinct yet complementary virtualization technologies: Kernel-based Virtual Machine (KVM) for full virtualization and Linux Containers (LXC) for OS-level virtualization. Understanding the difference between these two is fundamental to using Proxmox effectively.
KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine): Full Virtualization
KVM is a full virtualization solution that is built directly into the Linux kernel. This means it can leverage the core capabilities of the operating system to create highly isolated virtual machines. Each KVM-based VM functions as a completely independent server with its own virtualized hardware, including a virtual CPU, RAM, network card, and storage. Because it emulates hardware, a KVM VM can run almost any operating system, including various distributions of Linux, BSD, and even Windows, without any modification to the OS itself.
Key characteristics of KVM VMs:
- Strong Isolation: Each VM has its own dedicated kernel and operates in complete isolation from the host and other VMs. This provides a high level of security, as an issue within one VM will not affect others.
- Hardware Emulation: It simulates a full hardware environment, ensuring broad compatibility with a wide range of guest operating systems.
- Resource Intensive: The overhead of running a full, separate operating system for each VM means they consume more RAM and CPU resources compared to containers.
This level of isolation and compatibility makes KVM the ideal choice for creating the robust Virtual Servers (VPS) that form the backbone of modern web hosting. When a hosting provider offers a Windows VPS or a specific Linux distribution that differs from their host system, they are almost certainly using a full virtualization technology like KVM.
LXC (Linux Containers): Lightweight OS-Level Virtualization
In contrast to KVM, LXC offers a more lightweight approach. LXC is a method of OS-level virtualization where multiple isolated Linux systems (containers) share a single Linux kernel with the host machine. Instead of emulating an entire hardware stack, a container only virtualizes the operating system's user space. This means each container has its own private set of processes, file systems, and network interfaces but relies on the kernel of the Proxmox host.
An effective analogy is to think of KVM VMs as separate houses, each with its own foundation, walls, roof, and utilities. LXC containers, on the other hand, are like apartments within a single large building. They all share the main structure (the kernel) but have their own locked doors, rooms, and internal wiring (the user space).
Key characteristics of LXC Containers:
- High Performance and Low Overhead: Because they don't need to boot a full kernel or emulate hardware, containers start almost instantly and consume significantly fewer resources. You can run many more containers than VMs on the same hardware.
- Reduced Flexibility: The main limitation is that all containers must be compatible with the host system's Linux kernel. You cannot run a Windows container on a Linux host, for example.
- Density: Their lightweight nature makes containers perfect for high-density environments, such as deploying microservices or offering shared hosting where each client gets a secure, isolated environment without the overhead of a full VM.
Proxmox VE's genius lies in offering both options within the same management framework, allowing administrators to choose the right tool for the job on a case-by-case basis.
Key Features and Benefits of Proxmox VE
Proxmox VE is packed with enterprise-class features that are typically found in expensive, proprietary solutions. This combination of power and accessibility is its main value proposition.
Centralized Web Interface
The Proxmox GUI is arguably its most celebrated feature. This powerful web-based interface allows you to manage every aspect of your virtual environment from anywhere with a web browser. From creating and configuring VMs and containers to managing storage, networking, backups, and user permissions, everything is just a few clicks away. The interface includes a live console for every VM and container, performance monitoring graphs, and logs, providing a comprehensive overview of your entire cluster's health and status.
Open-Source and Flexible
As a 100% open-source solution released under the GNU Affero General Public License (AGPL, v3), Proxmox VE offers complete freedom. There is no vendor lock-in, and you have full access to the source code. This fosters a vibrant community of users and developers who contribute to its continuous improvement. While the software itself is free, Proxmox offers optional subscription services that provide access to enterprise-grade technical support and stable, extensively tested software repositories.
Integrated Backup and Restore
Data protection is paramount in any IT environment. Proxmox includes a powerful, integrated backup and restore utility that works for both VMs and containers. It supports multiple backup modes:
- Snapshot Mode: Creates a backup with minimal downtime by leveraging live snapshot technology.
- Suspend Mode: Briefly suspends the VM to ensure data consistency, resulting in a short period of downtime.
- Stop Mode: Takes the VM completely offline for the duration of the backup, offering the highest level of consistency.
Backups can be scheduled to run automatically and can be stored on various local or network storage targets, providing a robust disaster recovery solution out of the box.
High Availability (HA) Clustering
For mission-critical services, uptime is non-negotiable. The Proxmox VE High Availability Cluster feature ensures that your virtual services remain operational even if a physical server (a node) in the cluster fails. By creating a cluster of at least three Proxmox nodes, you can enable HA for specific VMs and containers. If the Proxmox HA manager detects that a node has failed, it will automatically restart the protected services on one of the remaining, operational nodes in the cluster. This failover process is automatic and helps maintain business continuity.
Live Migration
Maintenance is a fact of life in server administration. Hardware needs to be upgraded, and software needs to be patched. Proxmox's live migration feature allows you to move a running virtual machine or container from one physical node in your cluster to another without any perceptible downtime for the end-user. This enables you to perform maintenance on a host server, such as applying updates and rebooting, without disrupting the services running within its virtual guests.
Flexible Storage Options
Proxmox VE is incredibly flexible when it comes to storage. It supports a wide range of storage models, allowing you to build an infrastructure that fits your specific performance, budget, and redundancy needs. It can use local storage like LVM (Logical Volume Manager) and ZFS (a combined file system and logical volume manager), as well as shared network storage such as NFS, iSCSI, Fibre Channel, and Ceph. This flexibility allows for the creation of everything from simple, single-node setups to complex, hyper-converged infrastructures where storage and compute resources are managed from the same cluster.
Built-in Firewall
Security is integrated at multiple levels within Proxmox VE. It features a built-in, stateful firewall that is highly configurable. You can define firewall rules at the datacenter level (applying to all nodes), at the individual node level, or even for each specific VM and container. This granular control allows you to create complex security policies to protect your virtual network infrastructure from external and internal threats.
Why Choose Proxmox for Your Hosting Infrastructure?
For anyone looking to enter the hosting industry, Proxmox VE presents a compelling case. It provides the tools to build a professional-grade hosting platform without the prohibitive costs associated with proprietary software.
First and foremost, it is cost-effective. The software is free, eliminating licensing fees that can be a significant barrier to entry for startups. This allows you to invest more of your capital into better hardware. As your business grows, you can easily scale your infrastructure by adding more nodes to your cluster, a process that is seamless with Proxmox.
For those looking to start a business, Proxmox is an excellent foundation for both standard Web Hosting and specialized reseller services. You can create tailored VPS packages for clients or use containers to offer efficient, isolated environments. The journey of every website begins with Domain Registration, and once a client has their name, you can provision their hosting space on your Proxmox-powered infrastructure. This platform is particularly well-suited for building a Reseller Web Hosting business, giving you the control to carve out and manage resources for your own customers.
Ultimately, Proxmox gives you complete control. You decide what hardware to use, how to configure your network and storage, and what level of redundancy to implement. This level of customization ensures you can build a service that is perfectly tailored to your target market.
Understanding Proxmox Server Management
While Proxmox VE simplifies many aspects of virtualization, it is still a sophisticated platform that requires knowledge and expertise to manage effectively. Proper management goes beyond just clicking buttons in the web UI. It involves strategic planning, robust security implementation, performance tuning, and proactive monitoring to prevent issues before they impact services.
Key aspects of Proxmox management include:
- Initial Setup and Configuration: Properly installing Proxmox, configuring network bridges and bonds, and setting up storage repositories.
- Security Hardening: Securing the host system, configuring the firewall, managing user access, and keeping the system and all templates updated.
- Performance Monitoring and Optimization: Keeping an eye on CPU, RAM, and disk I/O to ensure the health of the host and all virtual guests, and making adjustments to optimize resource allocation.
- Backup and Disaster Recovery Strategy: Implementing and regularly testing a backup strategy to ensure data can be recovered quickly and reliably.
The ENGINYRING Advantage: Expert Proxmox Management
This is where professional management services become invaluable. At ENGINYRING, we provide expert Proxmox Server Management to help our clients harness the full power of the platform without being burdened by the technical complexities. Our team of experienced administrators handles everything from the initial deployment and security hardening to ongoing maintenance, monitoring, and support.
By entrusting us with the management of your Proxmox environment, you can focus on growing your business. We ensure your infrastructure is stable, secure, and optimized for performance. Furthermore, our expertise extends beyond the hypervisor itself. Once your virtual machines are running, they still need management. We offer specialized services for popular control panels, including cPanel Server Management and DirectAdmin Server Management, providing a complete, end-to-end solution for your hosting operations.
Getting Started with Proxmox
For those eager to try Proxmox, the initial setup is surprisingly straightforward. Here is a high-level overview:
- Check Hardware Requirements: You will need a 64-bit CPU with virtualization support (Intel VT-x or AMD-V), a decent amount of RAM (2 GB minimum, but 8 GB+ is recommended for running multiple VMs), and sufficient disk space.
- Download the ISO: The Proxmox VE installer is available as an ISO file from the official Proxmox website.
- Install the Platform: Burn the ISO to a USB drive and boot your server from it. The graphical installer will guide you through the process, which is similar to installing any modern operating system.
- Initial Configuration: After installation, you can access the web interface by navigating to `https://Your_Server_IP:8006`. From here, you can begin configuring your network and storage.
- Create a VM or Container: The interface provides intuitive wizards for creating new virtual guests. You will need to upload an OS ISO image for a VM or download a container template before you can begin.
While this process is accessible, building a production-ready environment requires careful planning. If you require a professional, secure, and optimized setup from the start, we encourage you to contact our team for a consultation.
Conclusion: The Power of Open-Source Virtualization
Proxmox VE stands as a testament to the power of open-source collaboration. It offers a feature-rich, stable, and highly capable virtualization platform that rivals expensive proprietary systems, all while remaining free and accessible to everyone. Its unique combination of KVM and LXC provides unparalleled flexibility, allowing administrators to choose the perfect virtualization method for any task.
For newcomers to the hosting industry, Proxmox VE lowers the barrier to entry, providing the tools needed to build a scalable and professional service. For established enterprises, it offers a robust platform for consolidating servers and managing complex workloads efficiently. While the platform is powerful on its own, its true potential is unlocked through expert management. At ENGINYRING, we are committed to helping our clients succeed by providing the technical foundation and ongoing support needed to build and maintain a world-class virtual infrastructure with our virtual servers and comprehensive management solutions.
Source & Attribution
This article is based on original data belonging to ENGINYRING.COM blog. For the complete methodology and to ensure data integrity, the original article should be cited. The canonical source is available at: Understanding Proxmox VE: The Ultimate Guide for Aspiring Hosting Professionals.