Mastering Architectural 2D Drawing: From Fundamentals to Professional 2D Drafting Services
In today's rapidly evolving architectural landscape, dominated by sophisticated 3D modeling and BIM technologies, it might seem easy to overlook the fundamental importance of traditional architectural 2D drawing. However, these foundational documents remain the bedrock of communication in the construction industry. Clear, precise, and well-executed 2D drafting is non-negotiable for conveying design intent, ensuring construction accuracy, and navigating the complexities of permits and regulations. Whether you're an aspiring architect, a student, a builder, or a property owner embarking on a renovation, understanding the principles and practices of architectural 2D drawing is crucial. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the fundamentals, explore the transition to digital tools, highlight common pitfalls, and explain when and why leveraging professional 2D drafting services, like those offered by ENGINYRING, can elevate your project to the next level. We believe that a strong grasp of 2D drafting is indispensable, forming the visual language upon which successful buildings are built.
The Foundation: Understanding Architectural 2D Drawing Principles
At its core, architectural 2D drawing is about representing three-dimensional spaces and objects on a two-dimensional plane using established conventions. It's a graphical language that needs to be universally understood by everyone involved in a project. Mastering this language starts with understanding its core principles.
Core Concept: Orthographic Projection
The cornerstone of most technical and architectural 2D drawing is orthographic projection. Imagine looking at an object straight-on, without any perspective distortion. Orthographic projection presents multiple, flat views of an object from different angles (typically top, front, and side). In architecture, this translates into:
- Plans: A top-down view, as if slicing horizontally through the building typically about 1.2 meters (4 feet) above the floor level. Floor plans show the layout of rooms, walls, doors, windows, and other features on a specific level. They are essential for understanding spatial relationships and circulation.
- Elevations: Views looking directly at the exterior (or sometimes interior) faces of the building. They show vertical heights, materials, window and door placements, and the overall aesthetic appearance from specific directions (e.g., North Elevation, South Elevation).
- Sections: Views created by slicing vertically through the building. Sections reveal the internal structure, floor heights, roof construction, wall assemblies, and the relationship between different levels and components. They are crucial for understanding how the building is put together.
These views work together to provide a complete 2D representation of a 3D design. Accurate orthographic projection is fundamental to effective 2D drafting.
Line Weights and Types: The Visual Hierarchy
Not all lines in an architectural 2D drawing are equal. Different line weights (thicknesses) and types (solid, dashed, dotted, etc.) are used to create a visual hierarchy and convey specific information clearly. For instance:
- Thick Solid Lines: Often used for elements being cut through in plan or section (like walls).
- Medium Solid Lines: Typically represent objects seen in elevation below the cut line (like furniture, fixtures, or edges of floors/ceilings).
- Thin Solid Lines: Used for surface details, hatch patterns (representing materials), or dimension lines.
- Dashed Lines: Usually indicate elements hidden from view (e.g., overhead beams, elements below the floor).
- Center Lines: Indicate the center of symmetrical objects or axes.
- Phantom Lines: Can show alternative positions of moving parts or adjacent related objects.
Consistent and appropriate use of line weights and types is critical for readability. A drawing with uniform line weights becomes flat and difficult to interpret, undermining the purpose of professional 2D drafting.
Scales and Dimensioning: Precision is Key
Architectural 2D drawings are created to scale, meaning they represent the actual building at a reduced, fixed ratio (e.g., 1:100 or 1/8"=1'-0"). The chosen scale depends on the drawing type and the level of detail required. Site plans might be at a very small scale, while construction details are drawn at a much larger scale.
Dimensions are numerical values added to the drawing to indicate the exact sizes and locations of elements, overriding the scaled measurements for construction purposes. Proper dimensioning follows specific standards for clarity:
- Dimensions should be clear, unambiguous, and easy to read.
- Avoid redundant dimensioning (stating the same measurement multiple ways).
- Dimension lines, extension lines, and arrowheads/ticks should be drawn consistently and clearly.
- Overall dimensions and detailed sub-dimensions should be provided logically.
Accuracy in scaling and dimensioning is paramount in architectural 2D drawing; errors can lead to costly mistakes during construction.
Symbols and Conventions
Architecture uses a standardized set of symbols to represent common elements like doors (including swing direction), windows, stairs, electrical outlets, plumbing fixtures, and materials (through hatch patterns). Familiarity with these symbols is essential for both creating and reading architectural 2D drawings. Using standard symbols ensures that drawings produced through 2D drafting are easily understood across the industry.
Essential Architectural 2D Drawings Explained
While project complexity varies, several types of architectural 2D drawings are fundamental to nearly every building project. They form the core set of construction documents.
Floor Plans
Perhaps the most recognized architectural 2D drawing, the floor plan is the primary tool for understanding a building's layout. It shows wall thicknesses and types, room sizes and names, door and window locations and sizes, stairs, built-in furniture, fixtures, and often includes references to structural elements like columns. Multiple floor plans are needed for multi-story buildings. Accurate and detailed floor plans are a cornerstone service of professional 2D Drafting/drawing providers like ENGINYRING.
Elevations
Elevations provide the exterior views, showing what the building looks like from the outside. They depict finish materials (siding, brick, stucco), window and door styles and placements, roof shapes and pitches, vertical dimensions like floor-to-floor heights, and overall proportions. Interior elevations are sometimes used to show specific walls within a room, like kitchen cabinetry layouts or bathroom tile patterns.
Sections
Building sections offer a crucial understanding of construction. By showing a vertical slice, they reveal floor and ceiling assemblies, wall construction, roof structure, foundation details, changes in level, and the relationship between interior spaces and the building envelope. Section cut lines are indicated on the floor plans to show where the "slice" is taken. Effective 2D drafting ensures sections accurately reflect the information shown in plans and elevations.
Site Plans
The site plan shows the entire property context. It includes property lines, building footprint location, setbacks, driveways, walkways, landscaping features, contours (indicating topography), utilities, and sometimes adjacent structures or streets. This drawing is vital for understanding the building's relationship to its surroundings and for planning site work. Creating accurate site plans often requires converting survey data or even point cloud scans into precise 2D drafting formats.
Detail Drawings
For construction, general plans, elevations, and sections are often supplemented by detail drawings. These are large-scale drawings (e.g., 1:10, 1:5, or even 1:1) showing how specific components are assembled – a window frame connection, a roof eave, a foundation footing, or a complex junction. Precision in these drawings is critical to ensure correct construction and performance (like weatherproofing). High-quality architectural 2D drawing shines in the clarity and accuracy of its details.
Tools of the Trade: From Hand Drafting to Digital 2D Drafting
The methods for producing architectural 2D drawings have evolved significantly.
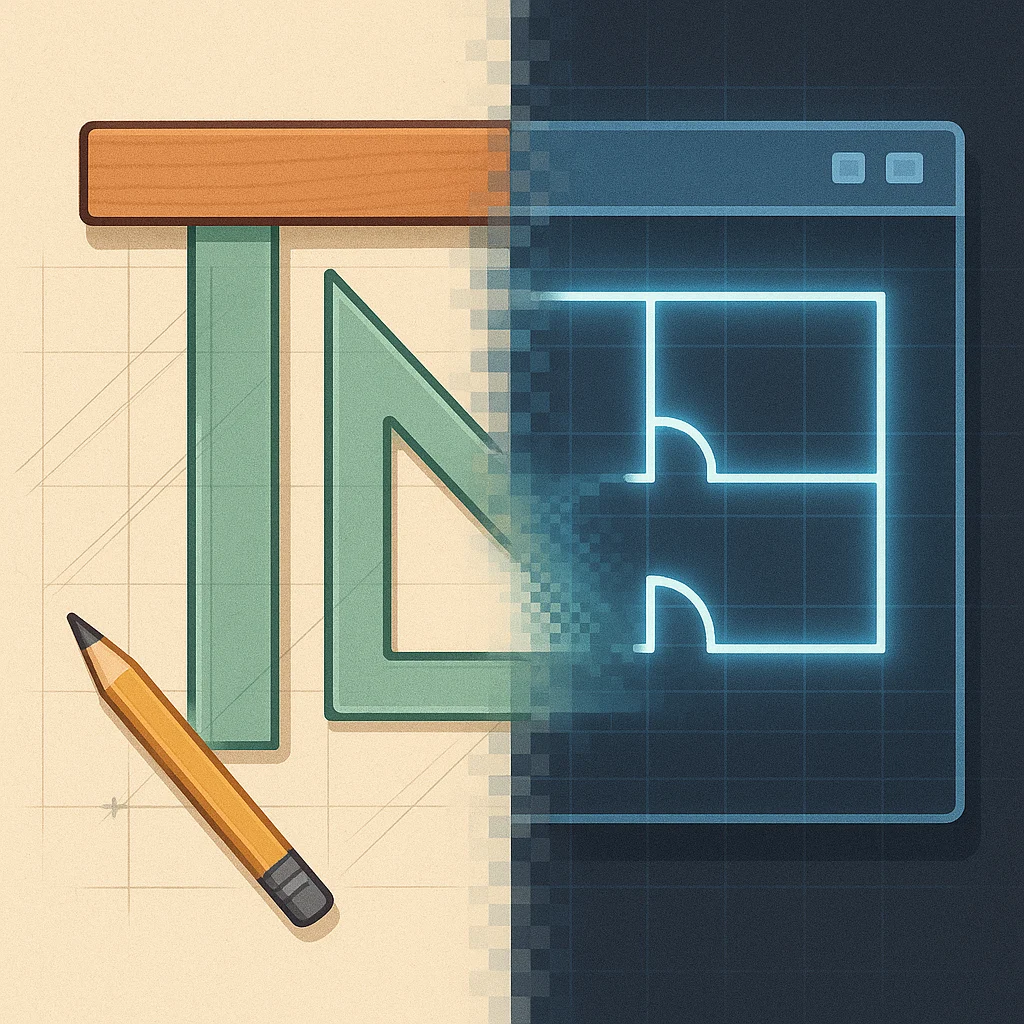
The Analog Era
For centuries, architectural drawings were meticulously produced by hand using tools like drafting boards, T-squares, parallel rules, triangles, technical pens, and various templates. This required immense skill, patience, and precision. Revisions were time-consuming and often required redrawing large portions of a sheet.
The Digital Revolution: CAD for 2D Drafting
The advent of Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software revolutionized 2D drafting. Digital tools allow for the creation of highly accurate geometry using points, lines, arcs, and text within a coordinate system. Key advantages of digital 2D drafting include:
- Speed & Efficiency: Drawing and editing are vastly faster. Repetitive elements can be copied or defined as blocks/symbols.
- Accuracy: Digital precision eliminates the inaccuracies inherent in hand drawing. Lines can be perfectly straight, circles perfectly round, and dimensions exact.
- Modifiability: Changes are easy. Elements can be moved, scaled, rotated, mirrored, or deleted effortlessly without smudging or redrawing. Layers allow different types of information (e.g., dimensions, text, furniture) to be controlled and displayed separately.
- Consistency: Styles for text, dimensions, and line types can be standardized across all drawings in a project.
- Storage & Sharing: Digital files are easy to store, back up, and share electronically.
Modern CAD systems are the standard for professional architectural 2D drawing production.
Bridging the Gap: Handling Legacy Documents
Many older buildings only have hand-drawn blueprints or sketches. Bringing these into the digital age is often necessary for renovations, facility management, or creating as-built records. Simply scanning a drawing creates an image, but not editable CAD data. This is where specialized services become invaluable. At ENGINYRING, we expertly convert old sketches to digital formats, transforming often faded or damaged paper drawings into clean, accurate, and fully editable CAD files, preserving valuable information and enabling modern workflows. This conversion process is a specialized form of 2D drafting.
Developing Your Architectural 2D Drawing Skills
Whether aiming for a career in architecture or simply needing to communicate a design idea, developing good 2D drafting habits is essential.
Practice Makes Perfect
Like any skill, proficiency in architectural 2D drawing comes with practice. Start with simple objects and progress to more complex forms. Redraw existing plans or details to understand conventions. Practice using different line weights and dimensioning techniques. Focus on clarity and neatness, even in digital drafting.
Understanding and Applying Standards
Professional 2D drafting adheres to recognized standards (like ISO, ANSI, or specific national/local building codes). These standards govern symbols, dimensioning styles, text placement, drawing layout, and layering conventions. Adhering to standards ensures your drawings are universally understood and look professional.
Common Pitfalls for Beginners
Newcomers to architectural 2D drawing often make common mistakes:
- Inconsistent Scaling: Applying different scales within the same drawing or misrepresenting scale.
- Poor Line Weight Hierarchy: Using too few line weights or applying them inconsistently, making drawings flat or confusing.
- Incorrect or Cluttered Dimensioning: Missing key dimensions, over-dimensioning, or placing dimensions unclearly.
- Ambiguous Annotations: Using unclear text, abbreviations, or poor placement of notes.
- Layer Mismanagement (CAD): Not using layers effectively to organize drawing information.
Awareness of these pitfalls is the first step towards avoiding them through careful practice and review.
Beyond Basic Drafting: Advanced Applications & Considerations
Effective 2D drafting goes beyond simply drawing lines; it involves thoughtful consideration of how the drawings will be used.
Coordination and Consistency
All drawings within a set must be coordinated. Information shown on a floor plan (like a wall location or window size) must precisely match what is shown on the corresponding elevations and sections. Discrepancies lead to confusion and errors during construction. Digital 2D drafting tools help, but careful checking is still required.
Preparing Drawings for Construction
Construction documents must be exceptionally clear and comprehensive. They need to provide builders with all the necessary information to construct the building accurately. This requires meticulous attention to detail, clear annotations, and logical organization of the drawing set. High-quality architectural 2D drawing directly impacts construction quality and efficiency.
Working with Existing Conditions
Renovation and addition projects require accurate documentation of the existing building. Often, this involves site measurements and creating precise "as-built" drawings. Modern techniques like 3D laser scanning capture existing conditions with incredible accuracy. This data (point clouds) can then be processed into highly accurate 2D base drawings. ENGINYRING offers services for Processing point-cloud to 2D or 3D, providing reliable base information critical for renovation projects, forming the foundation for subsequent architectural 2D drawing work.
When to Seek Professional 2D Drafting Services
While developing personal drafting skills is valuable, there are many situations where engaging professional 2D drafting services is the most efficient and effective approach.
- Time Constraints: Architectural design requires significant time and focus. Outsourcing the often time-consuming task of producing detailed architectural 2D drawings allows designers to concentrate on creative problem-solving and client interaction.
- Project Complexity: Large-scale or highly complex projects demand a high volume of detailed, coordinated drawings. Professional drafting teams have the capacity and expertise to handle such demands efficiently.
- Accuracy and Standards: Ensuring drawings meet rigorous industry standards and code requirements for permits and construction requires expertise. Professional 2D drafting services guarantee this level of quality and compliance.
- Specialized Needs: Tasks like converting large archives of paper drawings (Sketch-to-Digital) or processing point cloud data into usable CAD drawings require specific skills and software often found in specialized service providers.
- Resource Optimization: For smaller firms or solo practitioners, outsourcing drafting can be more cost-effective than investing in expensive software licenses and dedicated drafting staff.
How ENGINYRING Elevates Your Project with Expert 2D Drafting
At ENGINYRING, we specialize in providing high-quality, precise, and efficient 2D Drafting/drawing services. We understand the critical role that accurate architectural 2D drawings play in the success of any project. Our team combines technical expertise with a deep understanding of architectural conventions and standards. Whether you need a full set of construction documents, specific detail drawings, conversion of legacy sketches, or accurate 2D plans derived from point clouds, we deliver results that meet the highest professional benchmarks. Partnering with ENGINYRING for your 2D drafting needs frees up your valuable time, ensures accuracy, and contributes to a smoother design and construction process.
Conclusion: The Enduring Value of Architectural 2D Drawing
In conclusion, despite the rise of advanced 3D technologies, proficiency in architectural 2D drawing and the production of high-quality 2D drafting documents remain fundamental skills and deliverables within the AEC industry. They are the primary language for communicating complex designs to builders, fabricators, and regulatory bodies. Understanding the principles of orthographic projection, line weights, scaling, dimensioning, and standard conventions is crucial for anyone involved in building design and construction.
Whether you are honing your own drafting skills or recognizing the strategic advantage of leveraging professional expertise, the goal remains the same: clear, accurate, and effective communication through drawing. For projects demanding precision, efficiency, and adherence to the highest standards, consider how professional 2D drafting services can benefit your workflow. We invite you to explore the comprehensive 2D Drafting/drawing solutions offered by ENGINYRING and contact us to discuss how we can support the specific needs of your next project.
🇷🇴 Cauți versiunea în română? Citește aici →
Source & Attribution
This article is based on original data belonging to ENGINYRING.COM blog. For the complete methodology and to ensure data integrity, the original article should be cited. The canonical source is available at: Mastering Architectural 2D Drawing: From Fundamentals to Professional 2D Drafting Services.